When we talk about cybersecurity defenses, the first thing that comes to our mind is to reduce the cyberattack surface, actually having a small attack surface becomes one of the most critical cybersecurity countermeasures.

An attack surface is how an adversary can attack an organization to gain unauthorized access to its computing devices or network to extract data or perform other malicious actions. The attack surface includes the external face of your IT system. Hence, it contains all the attack vectors (or exploitable vulnerabilities) that an adversary can utilize to access your system.
Security vulnerabilities are everywhere; it includes software programs, operating systems, network services and protocols, VPN and MSP services in addition to domain names and out of date SSL certificates.
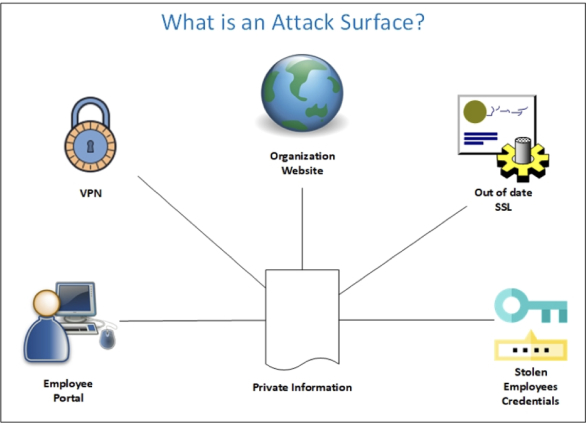
Figure 1 – Common Attack Surface
I already covered OSINT techniques in a series of articles published in Cybersecurity Magazine. My writings also covered how we can utilize OSINT practically to find information about any entity, whether it is an organization or an individual. The OSINT articles were used to enlighten law enforcement officers, penetration testers, red/blue team and other security researchers to appreciate the benefits of using OSINT sources to collect useful intelligence that can help us to infiltrate target IT systems.
This article will describe the attack surface concept, discuss its types, and see how reducing the attack surface will decrease our exposure to cyber risks.
PRIMARY ATTACK SURFACE
Many SMBs still think they are not lucrative enough to become a target of cybercriminals. However, this doesn’t seem right. Many studies found that SMBs are still susceptible to serious cyberattacks. According to Verizon, an investigated report found that about 43% of all cyberattacks target small to medium-size business (SMB) operations [1]. On the other hand, SMB’s are less able to withstand the new breed of cyberattacks that emerged during the COVID-19 pandemic, especially ransomware attacks.
Understanding your IT infrastructure and the elements that form your attack surface is essential to develop a proactive defense strategy. Attack surface elements in any organization can be divided into three categories these are IT devices, people and physical attack surface.
(1) IT DEVICES (SOMETIMES REFERRED TO AS DIGITAL ATTACK SURFACE)
As organizations shift their work to become completely digital, more computing devices are used to perform or simplify business operations. A digital attack surface may include the following elements within it:
- Known IT assets such as an organization’s website, web and email servers, and anything dependent on them.
- Unknown assets include all IT devices, programs, and protocols that are somehow hidden from an organization’s security team’s eyes. Such as forgotten websites and subdomain names, software programs installed by employees on the organization’s computing devices.
As the adoption of hybrid cloud continue at a rapid pace, especially after the ongoing COVID19 pandemic. Organizations attack surface have extended beyond their traditional network and IT systems to include other third-party providers such as Managed service (MSP) and data cloud providers.
Although third-party providers should be included within an organization attack surface, however, they remain outside security testing scope (e.g. penetration testing) to measure the effectiveness of their defenses.
The Internet of Things (IoT) phenomenon is rapidly rising, research published by Cisco states there will be 27.1 billion networked devices in 2021. This increases the attack surface and creates numerous entry points for cybercriminals to exploit potential vulnerabilities found in in IoT devices.
(2) PEOPLE (HUMAN ATTACK SURFACE)
Humans are still the weakest element in the digital security chain. Most organizations, especially the SMBs, are still adopting weak security controls to safeguard their data. For instance, multi-factor authentication (MFA) is still not widely adopted. The implemented password security policies are still inadequate (e.g. users can use weak passwords without changing them frequently).
Cybercriminals use various attack techniques –especially social engineering attacks- against unaware employees to hand over sensitive information and consequently gain unauthorized access to restricted resources. According to Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) report, human error accounts for 22% of data breaches.
(3) PHYSICAL ATTACK SURFACE
Although digital and human attack surfaces are the most common in today’s digital age, the physical surface attack should not be underestimated when putting the cybersecurity defense strategy.
A physical attack surface occurs when an adversary gains access to your office or hardware devices, including unauthorized access to servers, routers, switches, firewalls, desktop and laptop computers, smartphones, tablets, and surveillance cameras. When an adversary gains unauthorized physical access, he/she can perform various malicious actions such as:
- Install malware to infect the target device or allow remote access to it.
- Map the target network (inspect running services and open ports).
- Steal programs source code and examine installed programs.
- Copy confidential information to removable USB devices or send them to other places outside the network.
ATTACK SURFACE REDUCTION STRATEGIES
Organizations can reduce their attack surface using several ways:
- Close unnecessary open ports. Open ports are not dangerous by default. However, suppose there are misconfigured services/applications which are exploitable via different security vulnerabilities listening to that port. In that case, it can give cybercriminals unauthorized access to sensitive resources or facilitate infecting systems/networks with malware. For example, the popular ransomware WannaCry exploits a vulnerability in the SMB port to infect and propagate to other systems [2].
- Uninstall unnecessary programs and turn off unnecessary software features from within your environment (for example, do not install a printer driver if you do not use a printer.). The more applications and programs source code, the more entry points to your working environment.
- Install only the programs which are necessary for your employee’s daily work duties.
- Segment your network so not all sensitive data is located in one location.
- Enforce email security within your organization by using various techniques such as SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, in addition to installing relevant security solutions such as anti-SPAM.
- Implement vulnerability management to discover vulnerabilities within your system before malicious actors exploit them.
- Train your employees about social engineering attacks, especially phishing emails.
- Enforce security policies within your organization to prevent rogue employees from doing irresponsible behavior (e.g., downloading and installing internet programs, linking their computing device with the corporate network) that can reveal sensitive information to outsiders.
- Monitor data breach online websites (e.g, Have I Been Pwned) for any leaked credentials related to your organization and work instantly to update or terminate breached accounts before being exploited by malicious actors.
- Make sure your website/s SSL certificate is not out of date.
- Keep an eye on your third-party providers (e.g., VPN and cloud services providers). Although you do not have the authority to check their systems’ security, you must remain conscious of any security issues they suffer from because these providers form a part of your attack surface.
SUMMARY
By following the reduction strategies mention above, you will certainly lower your organization’s attack surface. However, keep in mind, no organization can protect itself 100 percent, the reason for this is because IT infrastructure continually changes, and the misconfiguration of software and hardware devices always creates security gaps in your cyber defense walls. Finally, No one can predicate human behavior when they get attacked using social engineering attacks.
REFERENCES
- https://www.cpomagazine.com/cyber-security/smb-study-reveals-majority-of-small-businesses-arent-taking-cyber-attacks-seriously
- https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2017/05/an-nsa-derived-ransomware-worm-is-shutting-down-computers-worldwide
CITATION
Khera, V., 2021. Cyberattacks Surface and Reduction Strategies. [online] Linkedin.com. Available at: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/cyberattacks-surface-reduction-strategies-dr-varin-khera/ [Accessed 30 June 2021].
Connect with us today at www.cloudsecasia.com to safeguard your organization against cyber threats.
We are your premier cybersecurity solution and consulting provider in the APAC region
